
When indulging in injection molded parts design, bosses are small but vital features. They’re the cylindrical bumps used for attachment, support, or positioning.
You’ll need to consider size, shape, and compatibility with the material for effective design in the injection molding process. A well-designed boss ensures stability without adding unnecessary weight.
What are Bosses?
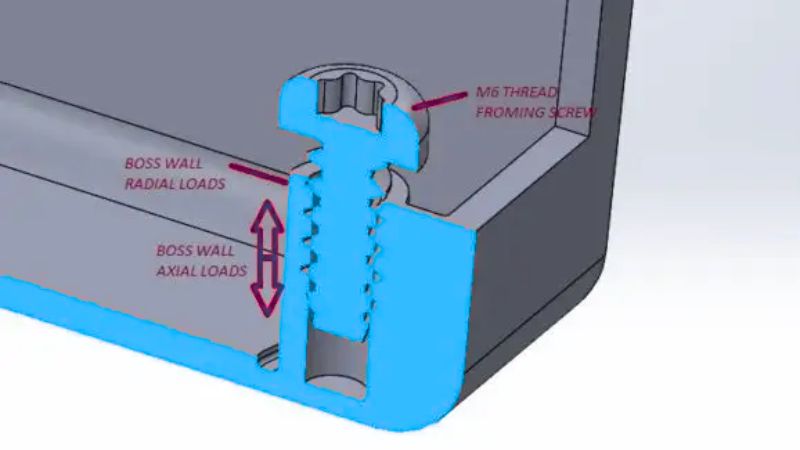
Bosses are key in providing attachment points in plastic components. They are usually cylindrical with a central hole to accommodate screws or fasteners.
Key Design Elements in Bosses
Draft angles help eject the part from the mold during manufacturing. Typically, the draft ranges from 0.5 to 3 degrees.
Without the right draft, parts can stick to the mold, causing defects or requiring additional force to eject, which may damage the part. Adjust draft angles based on the specific material and tooling. For aluminum molds, you might find a draft of 2 degrees to be most effective
Spacing between bosses also matters. You should maintain a safe distance to avoid compromising the part’s strength. A common guideline is to place bosses at least twice the nominal wall thickness apart.
Material is another point. Different plastics react to molding changes. Choose the materials to flow more easily, which allows for more intricate designs.
The material flow impacts how well the boss can form during injection molding. Good flow ensures complete mold filling and prevents defects.
Factors Affecting the Boss’s Strength
Wall Thickness and Its Impact
Wall thickness is a major factor in boss strength. You should aim to keep the boss walls about 40-60% of the nominal wall thickness of the part. This helps balance strength and avoid issues like sink marks or weak areas.
Aim for a uniform thickness, as this ensures even distribution of material. If you’re designing threaded bosses, make sure to have enough material for threads to engage properly.
Ribs and Gussets Integration
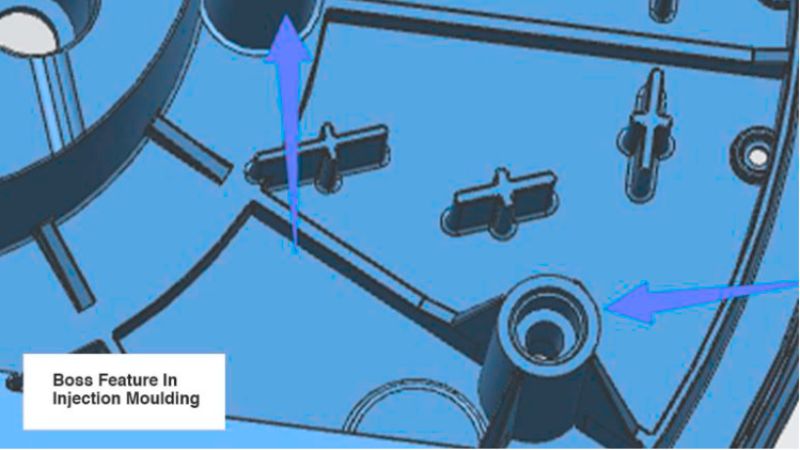
Integrating ribs and gussets into your design can greatly improve boss strength. Ribs help distribute stress evenly, reducing the chance of breakage.
Gussets add support by offering a triangular reinforcement at critical points. This can prevent deformation and enhance stability. To reduce stress concentration, avoid sharp corners in these areas. Use fillets to smooth out transitions and ensure stress is distributed more evenly.
Improving Assembly Processes
Threaded inserts are great for providing extra holding strength. They’re small parts you can add to a plastic boss to create a durable connection for screws.
Inserts are perfect when you need to assemble and disassemble parts multiple times without damaging the material. They also distribute force more evenly, reducing the risk of strain or wear on the surrounding area.
When using threaded inserts, plan their location carefully. Gussets or supporting ribs can be added to improve strength even further. This setup ensures that your assembly process remains smooth and efficient.
Optimizing for Durability
When designing for durability in plastic boss parts, focus on reducing stress concentrations and addressing ejection and surface finish.
These aspects help maintain structural integrity and improve the long-term performance of the components.
Avoiding Stress Concentrations
Stress concentrations can make plastic parts weak by causing cracks or breaks, especially around boss features. Using a fillet radius at the base of the boss helps spread out stress more evenly and prevents weaknesses.
Make sure the wall thickness is consistent and avoid sharp corners, which can lead to high stress areas. Use gradual transitions instead. Reducing stress concentrations in these ways can help avoid issues like sink marks and voids, contributing to a more durable end product.
Ejection and Surface Finish Concerns
Vent pins are important. They prevent air traps, which can cause issues like voids or poor surface finishes. Ensuring a smooth surface finish reduces the risk of small defects that might start stress fractures.
Designing for Manufacturability
Consider tooling carefully when designing your bosses. A sound tooling strategy ensures precision and reduces production time. Boss configurations and dimensions directly influence tooling design, especially in milling processes. Ensure bosses are not too tall, as this may lead to increased stress or require complex tooling adjustments.
Using circular ribs around the base can provide additional support and help distribute stress. Select the right cutter size and shape to ensure smooth edges and maintain the integrity of the boss features. Any errors in tooling can result in defective parts and reduced quality, affecting overall manufacturability. Focusing on these details helps in creating efficient and cost-effective designs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can you design a plastic boss for optimal use with self-tapping screws?
To create a solid design, make sure the boss has the right diameter and depth to accommodate the screws without causing stress or cracks. The material of the boss should also be compatible with the screw to prevent damage during installation.
What dimensions are critical when designing a screw boss for plastic parts?
Pay close attention to the height, diameter, and wall thickness of the boss. These dimensions should be tailored to work well with the intended fasteners and should distribute stress evenly. Correct dimensions help in preventing stripping or cracking.
How should plastic parts be designed to facilitate easier assembly?
Parts should be designed with alignment features to aid in precision during assembly. Use guide pins or slots to ensure parts fit together easily and correctly. This reduces the risk of incorrect installation and speeds up the assembly process.
parts should be designed with alignment features to aid in precision during assembly.
What considerations are important when selecting software for plastic design?
Look for software that offers simulation features to test design integrity and predict potential issues. The program should also be user-friendly, providing tools for analyzing stress and heat distribution. Additionally, integration with other tools can streamline your workflow.






